Hydrology network
Hydrological network includes watersheds with the corresponding major rivers, creeks, and lakes.
One important parameter of the hydrological network is the drainage density, which is a measurement of the total length of the streams in a drainage basin divided by the area of the basin. Drainage density is affected by climate, vegetation, topography, and geological characteristics of an area. A hydrological network can be traced on topographic maps and aerial photographs.
| Aim of the method/technique |
The proposed technique aims to define the hydrological network which can be used as a basic information on natural resources management. |
| Scale – spatial and temporal |
A detailed or semi-detailed map at the scale 1:10,000 or 1:50,000 can be useful for local and regional studies. A hydrological network usually presents a moderate spatial variability but limited temporal change.
|
| Brief description |
The hydrological network includes water-sheds with the corresponding major rivers, creeks, and lakes. Such information can be provided by the local water resources authorities and presented on maps. Furthermore, the hydrological network can be drawn on aerial-photographs as shown in Figure 1.
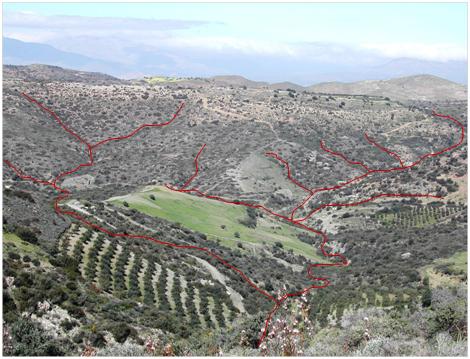 |
Figure 1. Example of a hydrological network and hydrological density drawn on a photograph (Source: C. Kosmas) |
|
| Data requirements |
The data required to draw a hydrological network are topographic maps, aerial photographs or remote sensing images. Furthermore hydrological data related to lakes and rivers can be obtained from local or regional administration authorities. |
| Main applications in cropland, grazing land and forests & shrubland regions |
Hydrology network is related to water resources availability of an area. Furthermore, drainage density is related to the erosion processes active in a watershed. The hydrological network is used to characterise water distribution in large forest environments as well as in setting up forest management plans.
|
| Strengths and weaknesses |
Data for the coarse hydrological network (main rivers and streams) are usually available at national or regional level. Detailed maps including the hydrological network of an area usually must be drawn by an expert in hydrology. |

